In recent years, a notable trend has emerged in society - the increasing number of individuals choosing to live alone. While living independently can offer many benefits, it also brings challenges, especially concerning emotional well-being. The surge in solo living raises important questions about loneliness, social connections, and public health implications.
Understanding the Loneliness Epidemic
A significant body of research highlights the detrimental effects of loneliness on health. According to a 2023 report from the U.S. Surgeon General, nearly half of American adults report feeling lonely. This epidemic of solitude isn’t merely a personal issue; it poses a broader public health challenge.
Loneliness has been linked to various health concerns, including anxiety, depression, and even premature death. The impact of social isolation can be profound, affecting not only mental health but physical health as well.
The Shift in Living Arrangements
One of the contributing factors to this rise in loneliness is the growing trend of living alone. Statistics reveal a dramatic shift in household dynamics. Over the past several decades, the proportion of households composed of married couples has decreased, while the number of individuals living solo has risen sharply. This change is particularly evident among women, who now constitute a significant segment of solo households.
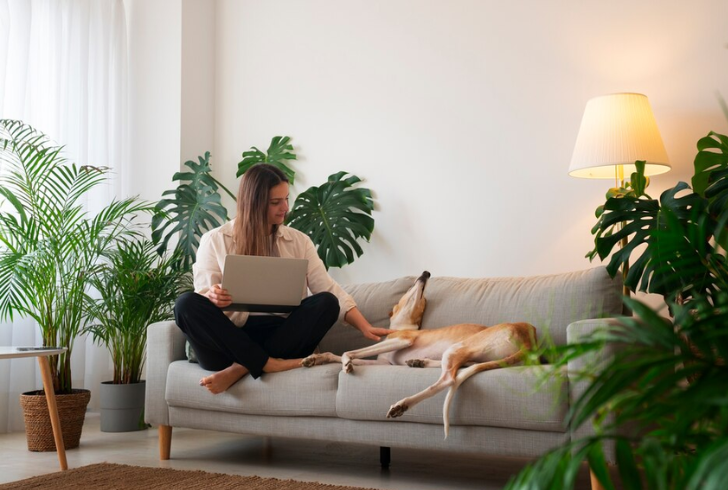

Freepik | In recent decades, married couple households have declined while solo living has sharply increased.
Key Statistics on Living Alone:
1. 1970 vs. 2022 - In 1970, 11.5% of women lived alone; by 2022, this figure climbed to 15.7%. For men, the percentage rose from 5.6% to 13.2% during the same period.
2. Aging Population - The aging Baby Boomer generation plays a pivotal role in this trend, as longer life expectancy leads to more individuals living alone, especially among older adults.
The Dynamics of Living Alone
While many people thrive in solitary living arrangements, the isolation that can accompany this lifestyle choice is noteworthy. Research shows that not everyone who lives alone experiences loneliness; however, the risk is undeniably higher. The experience of living alone varies widely based on factors such as age, gender, and personal circumstances.
Gender Differences in Solo Living
Interestingly, the trend of living alone differs by gender. Although women represent a larger proportion of solo dwellers, the increase in men choosing to live independently has been more pronounced in recent years. This trend could be attributed to various factors, including the growing acceptance of single living and changing societal norms regarding relationships and marriage.
Loneliness Across Age Groups
Loneliness is not confined to any specific age group; however, older adults are particularly vulnerable. A comprehensive study analyzing living arrangements over the past 170 years revealed that individuals born in recent decades are more likely to experience living alone later in life compared to previous generations. The shift in living patterns has been influenced by several factors, including changing family structures and societal expectations regarding marriage and companionship.
Insights from Recent Research
1. A recent study titled “170 Years of Living Arrangements in the U.S.” examined how living arrangements have evolved over time. The findings indicate that individuals born between 1980 and the present have seen a decline in expected years living with family members and an increase in solo living.
2. The research also highlights that individuals born in the early 1900s often spent more time living with extended family, showcasing the shift towards more independent living arrangements in contemporary society.
Implications of Living Alone
Living alone presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, it provides a level of autonomy and freedom that many cherish. On the other hand, it can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness, particularly during significant life events or transitions.
Strategies for Combating Loneliness
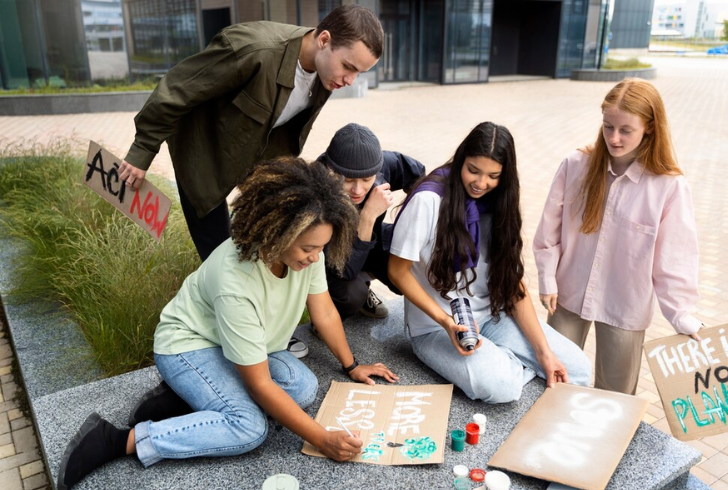

Freepik | Joining local activities or groups fosters social interaction and a sense of belonging.
To address the growing issue of loneliness among those who live alone, it is essential to foster social connections. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Join Community Groups - Engaging in local activities or groups can provide opportunities for social interaction and build a sense of belonging.
2. Volunteer - Contributing time to charitable organizations can connect individuals with others while promoting a sense of purpose.
3. Stay Connected - Utilizing technology to maintain connections with family and friends can help bridge the gap for those living alone.
The Role of Society
Addressing the challenges of loneliness requires a collective effort. Community initiatives aimed at creating inclusive environments and encouraging social interactions are vital. Programs that promote companionship, such as community centers or social clubs, can provide the support needed for individuals living alone.
Navigating the New Normal
As the trend of living alone rises, understanding its impact on mental and emotional health is crucial. While independent living can empower, it’s important to address the risks of loneliness. By fostering connections and supportive communities, we can mitigate these challenges and promote a healthier, more engaged society.
The rise of living alone reflects broader societal changes. Acknowledging the complexities of this lifestyle allows individuals and communities to ensure that living alone doesn't mean living in isolation. By nurturing connections, we can address loneliness and build a more connected, resilient society.